# 《Java极简设计模式》第21章:策略模式(Strategy)
作者:冰河
星球:http://m6z.cn/6aeFbs (opens new window)
博客:https://binghe.gitcode.host (opens new window)
文章汇总:https://binghe.gitcode.host/md/all/all.html (opens new window)
源码地址:https://github.com/binghe001/java-simple-design-patterns/tree/master/java-simple-design-strategy (opens new window)
沉淀,成长,突破,帮助他人,成就自我。
- 本章难度:★★☆☆☆
- 本章重点:用最简短的篇幅介绍策略模式最核心的知识,理解策略模式的设计精髓,并能够灵活运用到实际项目中,编写可维护的代码。
大家好,我是CurleyG~~
今天给大家介绍《Java极简设计模式》的第21章:策略模式(Strategy),多一句没有,少一句不行,用最简短的篇幅讲述设计模式最核心的知识,好了,开始今天的内容。
# 一、概述
定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并且使它们可相互替换。本模式使得算法可独立于使用它的类而变化。
# 二、适用性
1.许多相关的类仅仅是行为有异。“策略”提供了一种用多个行为中的一个行为来配置一个类的方法。
2.需要使用一个算法的不同变体。
3.使用算法的类不应该知道数据。可使用策略模式以避免暴露复杂的、与算法相关的数据结构。
4.一个类定义了多种行为,并且这些行为在这个类的操作中以多个条件语句的形式出现。 将相关的条件分支移入它们各自的Strategy类中以代替这些条件语句。
# 三、参与者
1.Strategy 定义所有支持的算法的公共接口。Context使用这个接口来调用某个ConcreteStrategy定义的算法。
2.ConcreteStrategy实现Strategy接口实现某具体算法。
3.Context 用一个ConcreteStrategy对象来配置。 维护一个Strategy对象的引用。 可定义一个接口让Strategy访问它的数据。
# 四、类图
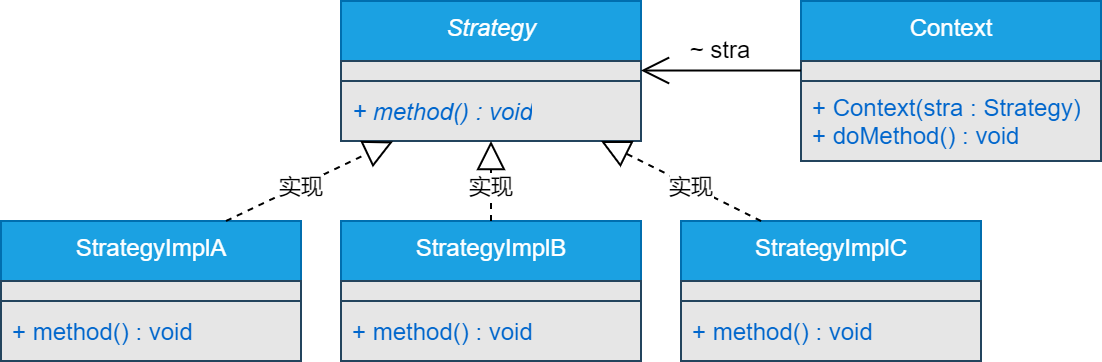
# 五、示例
Strategy
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Strategy
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public interface Strategy {
void method();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
ConcreteStrategy
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description ConcreteStrategy
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class StrategyImplA implements Strategy{
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("这是第一个实现");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description ConcreteStrategy
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class StrategyImplB implements Strategy{
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("这是第二个实现");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description ConcreteStrategy
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class StrategyImplC implements Strategy{
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("这是第三个实现");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Context
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Context
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Context {
private Strategy stra;
public Context(Strategy stra) {
this.stra = stra;
}
public void doMethod() {
stra.method();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Test
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 测试类
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Context ctx = new Context(new StrategyImplA());
ctx.doMethod();
ctx = new Context(new StrategyImplB());
ctx.doMethod();
ctx = new Context(new StrategyImplC());
ctx.doMethod();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Result
这是第一个实现
这是第二个实现
这是第三个实现
2
3
好了,今天就到这儿吧,相信大家对策略模式有了更清晰的了解,我是冰河,我们下期见~~
